Home
Operation Theater
Emergency Services
Rehabilitation Center
Rehabilitation Center
How we do
Welcome to MedicPlus
Medical Surgery
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit es.
- Dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur excepteur sint occaecat.
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit es.
Our Services
What we do
Who We Are
Meet our team
2319
Happy Patients1584
Doctors & Staffs13
Years With You3000
Hospital RoomsLatest Post
Recent News
Dr Tejas V Patel
Area of Specialization
- Radial angiography, angioplasty & stenting
- Complex Coronary Interventions like- Rotational Atherectomy, Left Main coronary intervention
- FFR Estimation, Coronary imaging – IVUS, OCT
- Transcatheter aortic valve replacement - TAVR, TAVI
- Device closure of ASD, VSD, PDA
- Other structural cardiac interventions- BMV, BPV
- Peripheral Angioplasty- Renal Angioplasty, Carotid Angioplasty, Limb Angioplasty
- Aortic aneurysm / dissection endovascular repair – TEVAR, EVAR
- Permanent Pacemaker Implantation & AICD Implantation (Automated Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator)
PROFESSIONAL EXPERIENCE
- Consultant Interventional Cardiologist, Care Institute of Medical Sciences (CIMS) Hospital, Ahmedabad – June 2015 till date
- Assistant Professor in Dept. of Cardiology, Christian Medical College (CMC) & Hospital, Vellore – Sept 2014 to May 2015
- Senior Registrar as DM Trainee in Dept. of Cardiology, Christian Medical College (CMC) & Hospital, Vellore – August 2011 to August 2014
- Registrar in Dept. of Medicine, M P Shah Medical College and Guru Gobind Singh Hospital, Jamnagar – 2006 to 2009
AWARDS & ACHIEVEMENTS
- Part of Heart transplantation team at CIMS hospital (CIMS is the only hospital in Gujarat achieved 9 heart transplantation so far) – Did observership at UMPC Presbyterian hospital, Pittsburgh, USA (2016) & Global Hospital in Chennai (2015)
- • Having experience of TAVR cases at CIMS hospital (CIMS is the only hospital in Gujarat has done maximum successful TAVR cases) – certified by Medtronic Academy TAVR program
- Have been Faculty & Course Director of Basic & Advanced Echocardiography Course by GE Healthcare Institute (2016 & 2017)
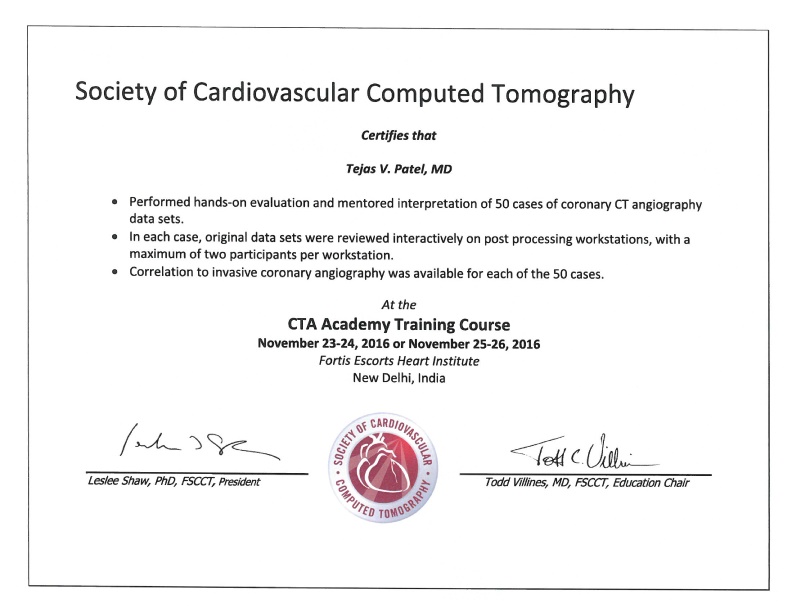
- • Have done CT coronary angiography course certified by Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography in 2016 at Fortis Escorts Heart Institute at New Delhi
- Awarded Associated Membership of Asia Pacific Vascular Society (2015)
- • Having experience for all complex peripheral interventions like TEVAR and EVAR – trained under Dr George Joseph at CMC Vellore at Tamil Nadu
- • Was part of STEMI INDIA program at CMC Vellore – was actively involved in development of similar program at CIMS hospital
- • Stood first in DM Cardiology exam held at CMC Vellore (2014) - awarded Dr. G. M. Cherian Gold Medal for "Best Outgoing Student in DM Cardiology"
- • Selected for zonal round (among top 10) in Torrent Young Scholar Award (TYSA) competition during both M.D. [Mumbai, 2009] and D.M. [Bangalore, 2013]
- • Stood 2nd in university in M.D. Medicine exam held at Saurashtra University at Gujarat (May 2009)
EARLY LIFE AND BACKGROUND
Born in the historical land of Saurashtra, Dr Patel finished his school education from Junagadh. He completed his MBBS and MD (Medicine) from MP Shah Medical College, Jamnagar. He achieved 2nd rank in the Saurashtra University in MD.
Dr Tejas V Patel pursued his super-speciality, DM in Cardiology from Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore; which is considered as one of the best medical institutions in India. He was awarded the prestigious “Dr G M Cherian Gold Medal” for ‘Best Outgoing Student in DM Cardiology’. He worked as Assistant Professor in this premier institute, after he finished DM. He spent almost four years at CMC, where he gained extensive experience in clinical, interventional and research work in the field of Cardiology.
Dr. Tejas V Patel has wide experience of performing coronary angiographies and coronary angioplasties – majority performed through transradial approach. He is also trained for various peripheral vascular interventions including intervention in Takayasu arterities, Aortic aneurysm and dissection – EVAR and TEVAR procedures. Dr. Patel has independently performed various diagnostic and interventional cardiac procedures such as percutaneous ASD/VSD/PDA device closure, Balloon Mitral,Pulmonary,Aortic Valvulotomy and cardiac catheterization study with or without oxymetry of various congenital heart diseases.
He has done more than 20,000 transthoracic echocardiography including paediatric echocardiography, Tissue strain and strain rate echo, 3D echo and trans-oesophageal echo (TEE). As per the patients treated by him, he has been rated as one of the best cardiologist in Ahmedabad, Gujarat.
Dr. Tejas V. Patel has participated in several original research projects and many of his papers have been published at National and International levels in reputed journals including ‘Journal of American College of Cardiology (JACC)’. He has also given presentation at various national conferences. He was selected for zonal round (among top 10) in Torrent Young Scholar Award (TYSA) competition during both M.D. at Mumbai, 2009 and D.M. at Bangalore, 2013.
EDUCATION
- Training at Seoul, Korea and Hong Kong University for advance technique in Angioplasty and stenting like OCT & FFR
- Observership in advance Heart Failure Management and Heart Transplantation at University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC), Pittsburgh, USA
- DM Cardiology: Christian Medical College, Vellore, Tamilnadu, India (2011-2014)
- MD (Medicine): M P Shah Medical College & Guru Gobind Singh Hospital, Jamnagar, Gujarat (2006-2009)
- MBBS: M P Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat (1998-2004)
- Secondary and Higher Secondary Education (School): 1996 passed 10th from Carmel Convent School, Junagadh, Gujarat & 1998 passed 12th from Swami Vivekanand High school, Junagadh, Gujarat
RESEARCH – PUBLICATIONS
- Co-investigator at CMC in Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) funded MACE PILOT study [Registry on management of acute coronary event (MACE Registry) - Pilot Phase]
- Varghese M. J., Patel T. V., George P. V., Pati P. K. & Jose V. J. Mammoth Right Atrium. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 63, e21 (2014).
- George P. V., Patel T. V. Impact of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in the management of post myocardial infarction ventricular septal rupture- a case report. Med ej. 2014 July-Aug; vol-4.
- Shah V, Patel T.A case of Malabsorption Syndrome (MAS) due to Tropical Sprue. JCDR. 2009 Apr; 3:1445-1448.
Presentations
- Invited as Faculty in India Live 2018 conference at Chennai for presentation in section ‘Meet the Expert – CD presentation’ ; presented- “Simple calcific RCA lesion – Never underestimate”
- Invited as Faculty in India Live 2018 conference at Chennai for presentation in section ‘Meet the Expert – CD presentation’ ; presented- “Simple Procedure – Dreaded Complication”
- Invited for poster presentation in American College of Cardiology 65th Annual Scientific Session (ACC.16) at Chicago in April 2016. [Subject - Serum Procalcitonin - A Novel Biomarker in ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction to Predict In-hospital and 30days Outcomes]
- Invited for case presentation and as a Faculty of the Year at the 21st CardioVascular Summit-TCTAP 2016 hosted by CardioVascular Research Foundation (CVRF) at Seoul, Korea.
- Exclusive CO2 angiography and bilateral renal artery stenting in a rare presentation of Takayasu arteritis -selected for challenging case presentation in INDIA LIVE 2015
- Lysosomal storage disease –a rare cause of Hepatosplenomegaly. APGCON 2008 (Poster presentation).
- A rare case of hepatolenticular degeneration (Wilson’s disease). APGCON 2008 (Poster presentation).
CERTIFICATION & AWARDS
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
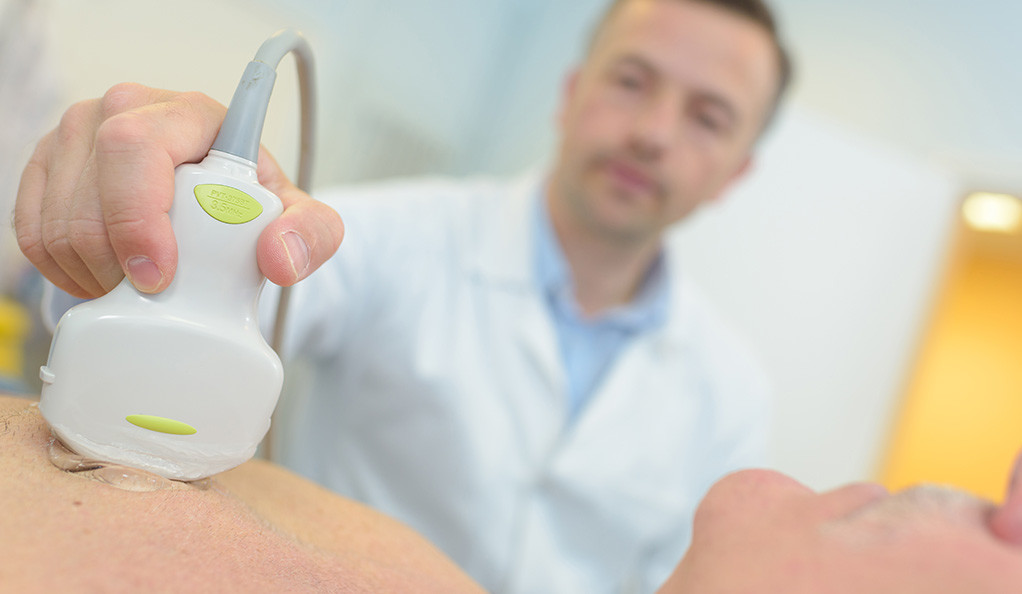
Echocardiography or simply an Echo is a sonography of the heart.
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
Echocardiography or simply an Echo is a sonography of the heart. It uses sound waves to create moving pictures of your heart. An echocardiogram can be done in the doctor’s office or a hospital. It requires undressing from the waist up and to lie down with turning left on an examination table or bed.
WHAT CAN ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY SHOW?
- The size and shape of your heart
- Overall pumping of your heart
- Any wall or section of your heart is weak and not working correctly
- Condition and function of your heart’s valves
- Any blood clot or tumors or any focus of infection in your heart
- Any birth defect in your heart like holes in the heart
WHY DO I NEED ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TEST?
Your doctor may use this test to look at your heart’s structure and function in variety of diseases. This test may be needed if…
- You have a heart murmur
- You have had a heart attack
- You have unexplained chest pains, breathing problems, palpitation, fainting attacks (syncope)
- You have cardiac valve problem
- You have a congenital heart defect / birth defect
DIFFERENT MODES OF ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
Depending on what information your doctor needs, you may have one of the following kinds of echocardiograms:
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE): This is routinely done in which a probe (transducer) is placed on your chest. The probe sends special sound waves, called ultrasound, through your chest wall to your heart. As the ultrasound waves bounce off the structures of your heart, a computer in the echo machine converts them into pictures on a screen.
Trans-esophageal echocardiography (TEE): During this test, the transducer is attached to the tip of a flexible tube. The tube is introduced through your mouth into your food pipe (esophagus). TEE shows clearer pictures of your heart, because the probe is located closer to the heart. This allows your doctor to get more detailed pictures of your heart. Drug spray is given to your throat prior to the procedure for prevention of discomfort and pain.
Stress echocardiography: During this test, an echo is done both before and after your heart is stressed either by having you exercise or by injecting a medicine that makes your heart beat harder and faster. A stress echocardiogram is usually done to find out if you might have decreased blood flow to your heart due to possible blockage in the arteries supplying blood and oxygen to heart muscle.
Three-Dimensional (3D) echocardiography: A three-dimensional (3D) echo creates 3D images of your heart.
ANGIOGRAPHY
Coronary angiography is a test that uses special dye and special x-rays to show the insides of your coronary arteries.
ANGIOGRAPHY
WHAT IS CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY?
Our heart pumps blood (and oxygen) to all the body organs. Heart muscle also needs oxygen for the function of pumping, which is supplied to the heart by Coronary arteries. Coronary angiography is a test that uses special dye and special x-rays to show the insides of your coronary arteries. The facility where such test is possible with special x-ray machine is called ‘Cath lab’ (catheterization laboratory).
In this procedure, a thin, hollow tube called a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel from your arm or groin. The tube is then advanced and threaded into your coronary arteries. Then dye is injected and x-ray pictures are taken while the dye is flowing through the coronary arteries. This helps doctors see blockages in the arteries. When the angiogram is over, the catheter is removed and pressure bandage is applied at the puncture site.
BEFORE AND AFTER CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY
Prior to the angiography, you may need some blood tests and ECG (cardiogram). You may be asked to stop eating and drinking for few hours before the test. You may be asked to shave both groins and arms before the test. If you are pregnant, you need to inform the doctor prior to the test.
Before the test starts, you can be given a mild sedative, which helps you to be relaxed. You’re fully awake during the procedure, and it causes little or no pain. It takes only few seconds to finish this test. Generally the risk of serious complications is very low. You can be discharged on the same day of procedure. You should drink plenty of fluids to help flush the dye from your body.
Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for several days. Your puncture site is likely to remain tender for a while. There can skin discoloration and a small swelling for few days at the puncture site.
WHEN TO DO CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY?
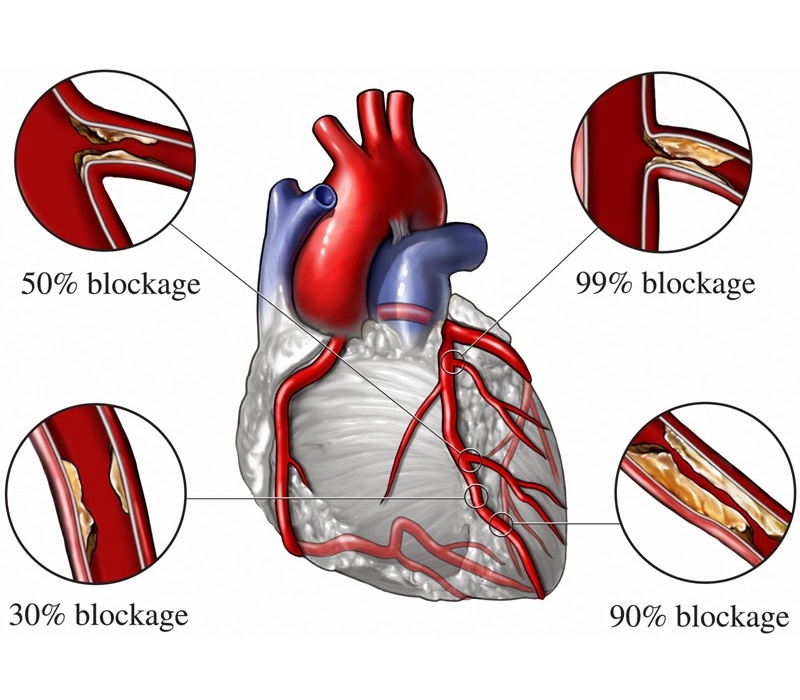
Coronary angiography is considered as a ‘gold-standard’ test to diagnose blocks in the artery of your heart. When cholesterol gets deposited in the wall of your coronary arteries (called as plaque), it causes narrowing of the lumen of arteries; which is called ‘Coronary artery disease (CAD)’. Narrowing of the artery causes reduction of oxygen-rich blood supply to your heart.
This can cause chest pain or discomfort called ‘Angina’. Sometimes a blood clot develops on the surface of plaque and it can partially or completely block blood flow through the coronary artery. This can compromise the viability of heart muscle and in few minute your heart muscle stops working. This can cause the most severe form of heart attack called ‘Myocardial infarction (STEMI)’. Coronary angiography is very useful test to diagnose above conditions.
ANGIOPLASTY WITH STENTING
Angioplasty is not a major surgery, it can be done from the same puncture (in arm or groin) done for angiography.
ANGIOPLASTY WITH STENTING
WHAT IS CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY / PAMI?
When cholesterol gets deposited in the wall of your coronary arteries (called as plaque), it causes narrowing of the lumen of arteries. This can reduce blood flow to your heart and cause chest pain (angina) or heart attack (myocardial infarction). Coronary angioplasty, also called PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty) is the procedure which opens blocked arteries (by tiny balloon & stent) and restores normal blood flow to your heart muscle. In emergency situation like, heart attack (myocardial infarction/STEMI), angioplasty should be done as soon as possible and it is called as PAMI (Primary Angioplasty in Myocardial Infarction).
HOW CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY IS DONE?
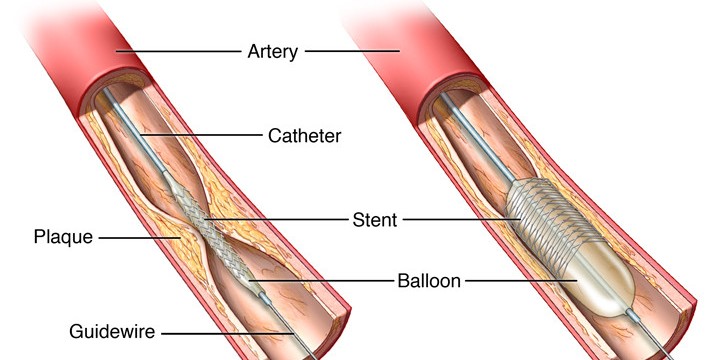
Angioplasty is not a major surgery, it can be done from the same puncture (in arm or groin) done for angiography. Patient remains fully awake throughout the procedure. Whole procedure is performed with the help of special x-ray machine in cardiac cath lab (cardiac catheterization laboratory). In this procedure, a thin, hollow tube called a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel from your arm or groin. The tube is threaded into your coronary arteries and tiny wire is advanced into the artery where the block is situated. The blocked artery is then opened by inflating a tiny balloon in it. Angioplasty is often combined with the placement of a stent. The whole procedure usually takes 30-60 minutes.
CORONARY STENT
A stent is a short, metal mesh tube that acts like a scaffold to help keep your artery open. Stent remains in the body permanently. There are two main types of stent:
- BMS – Bare metal stent or uncoated stent
- DES – Drug eluting stent or medicated stent; which is coated with special medication that reduces the risk of the artery becoming blocked again
There are certain stents which are made from special materials that get dissolved or be absorbed in the body. This type of stent disappears completely from the body after few months.
PRECAUTIONS AFTER ANGIOPLASTY & STENTING
You will usually remain hospitalized for one day while your heart is monitored and your medications are adjusted. You will normally be able to go home the day after the procedure. You will need to avoid heavy lifting, strenuous activities and driving for few days.
The most important thing is that you closely follow your doctor’s recommendations about your drugs, especially with blood-thinning medications such as Aspirin and clopidogrel or similar medications like Ticagrelor/Prasugrel. Those who have had stent placement will need a blood-thinning medication for a year or longer in some cases. If you have any doubts or if you need any surgery, talk to your cardiologist before stopping any of these medications.
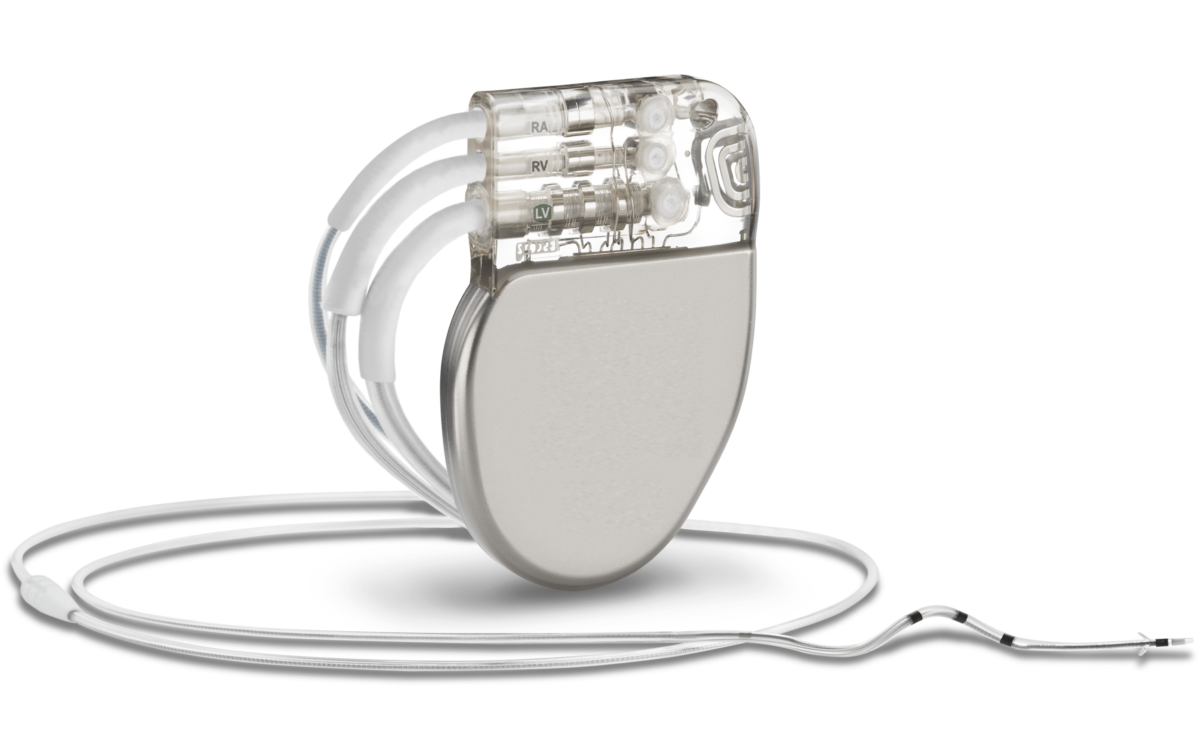
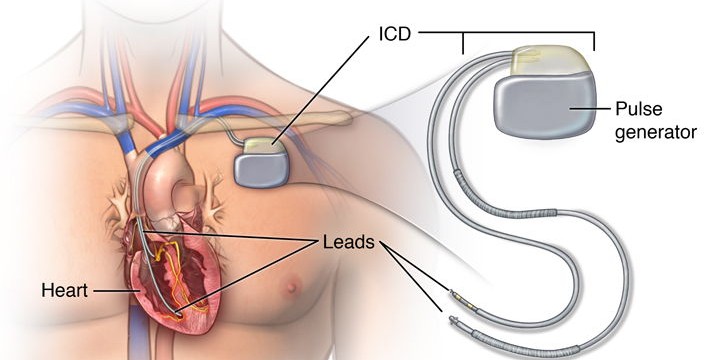
TEMPORARY AND PERMANENT PACEMAKER IMPLANTATION
A pacemaker is a small device, smaller than the size of your fist; that’s placed under the skin near your heart to help control your heartbeat.
TEMPORARY AND PERMANENT PACEMAKER IMPLANTATION
WHAT IS A CARDIAC PACEMAKER?
Every heart has its own internal electrical system and natural pacemaker that regulates the rate and rhythm of your heartbeats. With each heartbeat, an electrical signal spreads from the top of your heart to the bottom. As the signal travels, it causes the heart to contract and pump blood.
However, sometimes your heart beats too slowly that it may not be able to pump enough blood to the body. A pacemaker can correct this problem. It is a small device that sends electrical impulses to the heart muscle to maintain adequate heart rate and rhythm. A pacemaker is a small device, smaller than the size of your fist; that’s placed under the skin near your heart to help control your heartbeat.
WHO NEEDS A PACEMAKER?
Doctors may recommend pacemakers to you for many reasons. The most common reasons are very low heart rate and heart block. Heart block is a problem in the electrical system of the heart so that electrical signals cannot reach from upper chambers to the lower chambers of your heart. As a consequence pumping of your heart is reduced. Heart block can happen as a consequence of advanced aging, severe heart attack, or certain neuromuscular disorders.
Pacemakers can be temporary or permanent. Temporary pacemakers are used to treat short-term heart problems and during emergencies. They might be used until your doctor can implant a permanent pacemaker or until a temporary condition goes away.
TYPES OF PACEMAKER
There are different types and modes of pacemaker. Your doctor will decide what type of pacemaker is best for you based on your heart condition.
- Single-chamber pacemaker: It contains only one lead in the right side of the heart.
- Dual-chamber pacemaker: It contains two leads, one in the upper and another in the lower chamber of the right side of the heart.
ICD & CRT IMPLANTATION
It is a special type of pacemaker, which is useful to control very fast heart rate which can occur in certain diseases.
ICD & CRT IMPLANTATION
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD): It is a special type of pacemaker, which is useful to control very fast heart rate which can occur in certain diseases. Very fast heart rate of lower chamber of the heart (ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation) is very serious and life threatening condition. If it is not treated promptly, patient can become unconscious or even die in few minutes. ICD is a special device similar to pacemaker can immediately deliver electrical impulse or shock to the heart when it detects this serious rhythm problem.
Biventricular pacemaker / Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT): It contains three leads – two in upper and lower chambers of right side of the heart and third placed in left side of the heart. It is useful in the patient of heart failure. A biventricular pacemaker paces both ventricles so that all or most of the ventricular muscle pumps together. This allows the heart to pump blood more effectively.
SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS
Physical Activity: Do not hold your arm above shoulder level for 3-4 weeks after pacemaker implantation. Avoid activities that require pushing or pulling heavy objects. Ask your doctor how much and what kinds of physical activities are safe for you. Self-driving should be avoided if you have implanted ICD.
MRI: Avoid standing near strong magnetic field including MRI rooms if you have pacemaker implanted. All pacemakers are not MRI compatible and you cannot undergo MRI if you have pacemaker which is not compatible with MRI. Even though you have MRI compatible pacemaker, consult your cardiologist before undergoing any MRI.
Electrical Interference:
- It is safe to talk on a cellphone, but avoid placing your cell phone or MP3 players/iPods directly over your pacemaker implantation site.
- Passing through an airport metal detector won’t interfere with your pacemaker, although the metal in it may sound the alarm. Security staff can check you with a metal detector wand as long as it isn’t held for too long over your pacemaker site. You should avoid sitting or standing close to a security system metal detector. Notify security staff if you have a pacemaker. To avoid potential problems, carry an ID card stating that you have a pacemaker.
- Stay at least 2 feet away from industrial welders, high-voltage transformers or motor-generator systems.
- Shock-wave lithotripsy and electro-cautery used in surgery can interfere with the function of your pacemaker. Let all of your doctors, dentists, and medical technicians know that you have a pacemaker.
DOES PACEMAKER HAVE BATTERY? HOW LONG WILL MY PACEMAKER LAST?
Once your pacemaker is implanted, the battery should last 5-10 years, depending upon how frequently you need pacing. When a pacemaker’s battery wears out, your doctor will replace the generator along with the battery. Your doctor can tell you whether your pacemaker or its wires need to be replaced after interrogation of your pacemaker.
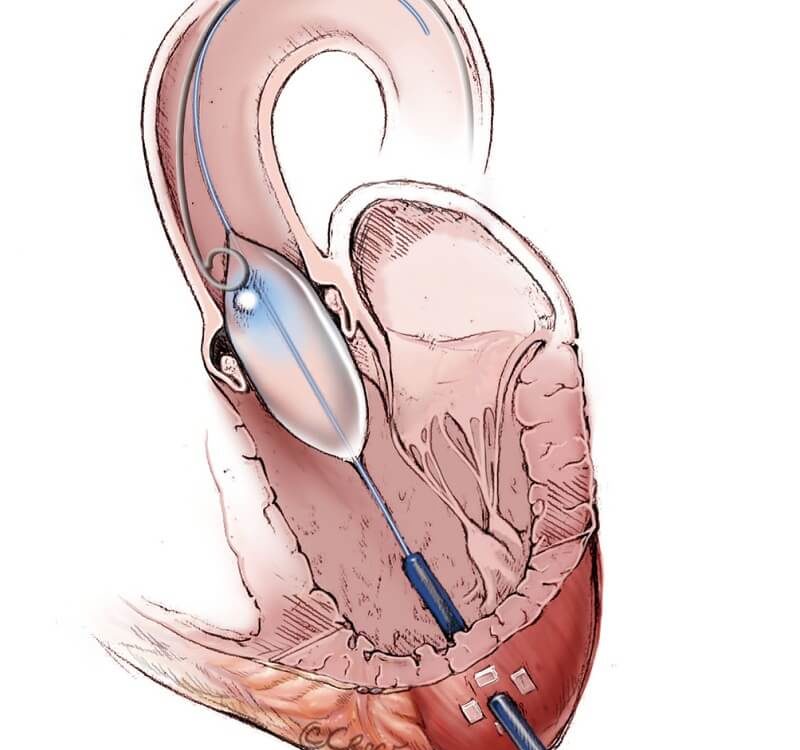
BALLOON VALVULOPLASTY
Balloon Valvuloplasty (or valvulotomy) means dilation of narrowed cardiac valve with balloon.
BALLOON VALVULOPLASTY
Balloon Valvuloplasty (or valvulotomy) means dilation of narrowed cardiac valve with balloon. This modality of treatment useful in certain diseases of valves of the heart in which valve stenosis occurs either due to birth defect or due to acquired inflammation. This procedure is usually done by a small injection from your groin region under local anesthesia. Mild sedation is given to you for pain relief. You remain conscious during the procedure; unlike valve replacement surgery which is an open heart surgery and requires general anesthesia.
In this procedure a long, thin tube (catheter) is inserted from your groin. Then a balloon is advanced to your heart and passed across the diseased narrowed valve. Now the balloon is inflated to open or stretch the valve. The balloon is then deflated and it is removed along with the catheter from your body. Balloon valvuloplasty relieves many symptoms of heart valve disease, but may not completely cure it.
Balloon valvuloplasty is useful for all 4 cardiac valves named Mitral, Aortic, Pulmonary and Tricuspid. It is commonly done in rheumatic heart disease involving mitral valve causing mitral stenosis (narrowing of mitral valve). Balloon aortic valvuloplasty and ballon pulmonary valvuloplasty are commonly performed in children.
If you have any heart valve problem, you should consult your cardiologist. Cardiologist will perform Echocardiography to look at the problem in the valve and then can advise whether you should get benefit of balloon valvuloplasty and whether it is an appropriate treatment for your condition.
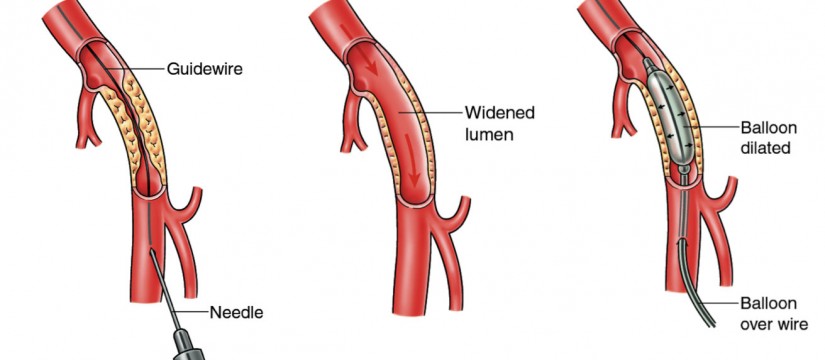
PERIPHERAL ANGIOGRAPHY AND ANGIOPLASTY
Peripheral angiography is used to check condition of blood vessels supplying your legs and arms.
PERIPHERAL ANGIOGRAPHY AND ANGIOPLASTY
A peripheral angiography is a test similar to coronary angiography. Unlike coronary angiography which is used to look the condition of artery supplying your heart; peripheral angiography is used to check condition of blood vessels supplying your legs and arms. This test uses special x-ray machine and it is performed in cath lab.
WHEN TO DO PERIPHERAL ANGIOGRAPHY?
Peripheral angiogram is useful test for the diagnosis of peripheral artery disease (PAD). PAD is a disease in which cholesterol and/or blood clots cause narrowing of the lumen of the artery supplying blood to your the legs or arms. Such blocks in the artery cause muscle pain or cramping in legs or arms on activity, such as walking or climbing stairs, and disappears after a few minutes of rest (intermittent claudication).
Once the disease progresses, you may feel pain even at rest. Critical narrowing of the artery can cause ulcer or gangrene formation in your leg.
PERIPHERAL ANGIOPLASTY
Treatment for peripheral artery disease includes special drugs that reduce the pain in your leg while walking or climbing stairs. If symptoms are not relieved with the medications then angioplasty or surgery is indicated. In peripheral angioplasty, a catheter (thin hollow tube) is inserted through your groin. Then in this catheter a balloon is advanced in the blocked artery.
The balloon is then inflated; this widens the artery and reduces the block. A stent (a small mesh tube) may be placed in the artery during angioplasty. A stent helps keep the artery open and prevent re-occlusion.
CATHETER-DIRECTED THROMBOLYSIS (CDT)
Sometimes your artery may be blocked due to blood clot in it. In such situation injection of a clot-dissolving drug (clot busters) into your artery through a catheter (thin hollow tube) is done to break the clot and to restore the blood flow in the blocked artery.
























Recent Comments